



The World is Running Out of Effective Antibiotics
In the global race against antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and related
healthcare-associated infections (HAIs), we provide diagnostic solutions
that quickly and accurately identify pathogens to enable the right
isolation and treatment before it's too late.
Join us in the race - MORE results, LESS spread.
True Scale of the AMR Threat
By the year 2050, it is estimated that 10 million people will die annually because of drug-resistant infections.1 Following recently published data in the landmark Lancet GRAM report, we know we are now far closer to this figure than ever realised.2
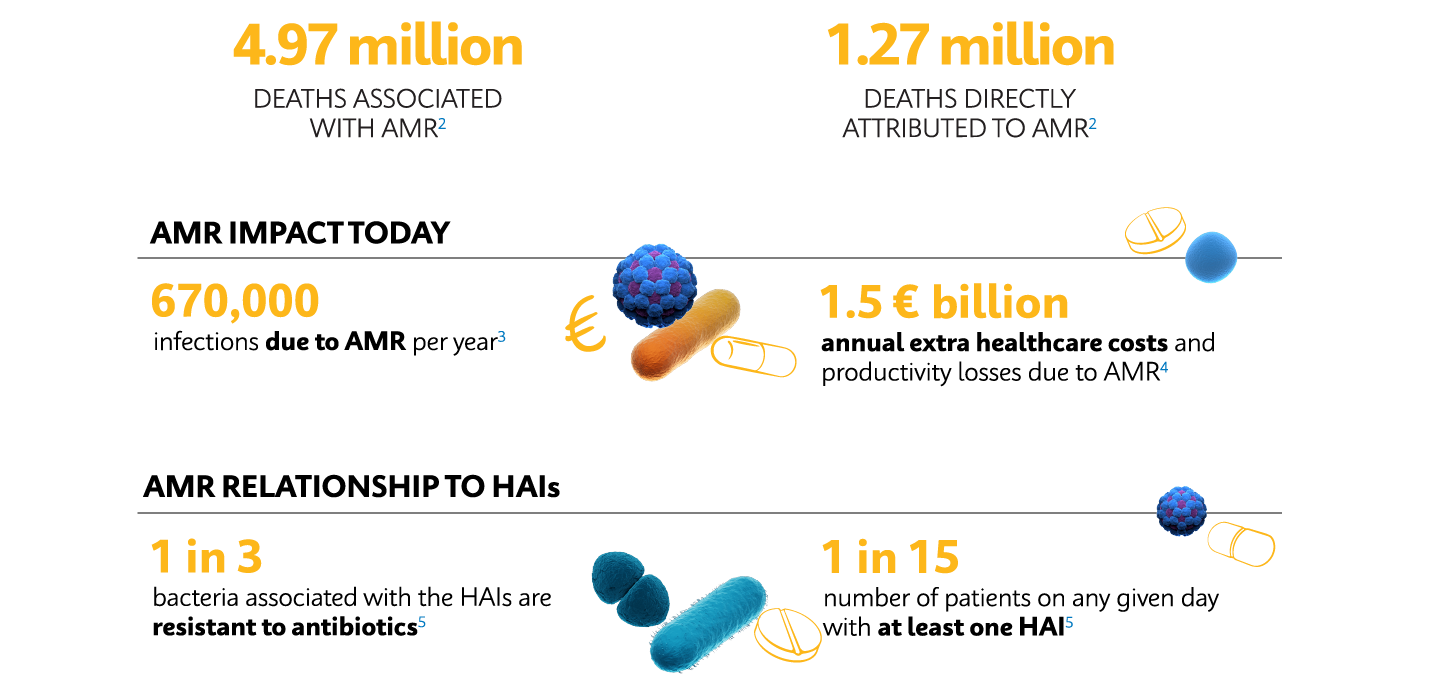

What is the Silent AMR Pandemic?
The burden of AMR is comparable to that of HIV, TB, and Influenza combined. Video courtesy of the ECDC.

What is the Silent AMR Pandemic?
The burden of AMR is comparable to that of HIV, TB, and Influenza combined. Video courtesy of the ECDC.
COVID-19: AMR Legacy
The COVID-19 pandemic has elevated concerns over AMR and antibiotic-associated adverse events, with surges in antibiotic prescribing, hospitalizations, and drug-resistant bacterial transmissions.6,7

COVID-19 hospital-admitted patients with a secondary bacterial infection.6

COVID-19 hospital-admitted patients who received antibiotics.6

COVID-19 ICU-admitted patients who received antibiotics.8
Future Preparedness
Throughout the COVID-19 pandemic, PCR testing emerged as the superior assay format in terms of accuracy and sensitivity, forming the backbone of nationwide screening regimens.9
Most hospital laboratories now have the capability, awareness, and even the infrastructure to carry out molecular testing, so that shifting from culture- to molecular-based workflows to accelerate turnaround times is more feasible than ever before.



Outbreak Risks
Superbug outbreaks and AMR pose one of the greatest challenges to the healthcare systems, and national elective recovery plans. With the right test, quickly and accurately identify pathogens in under one hour* to enable the right isolation and treatment, keeping wards open, reducing hospital costs, and stopping the spread of resistance.
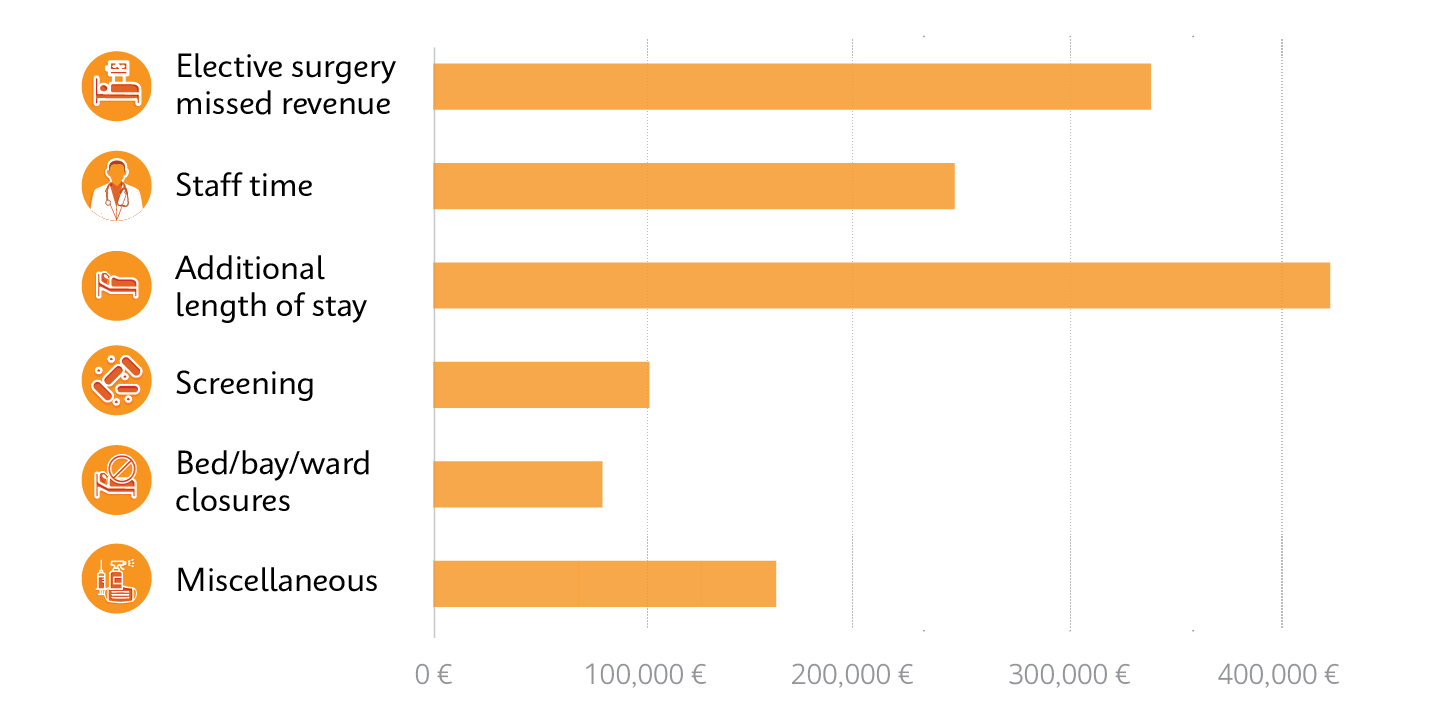
Cost breakdown from a single outbreak of a rapidly spreading superbug, carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales (CPE), which exceeded €1,000,000 over 10 months.10
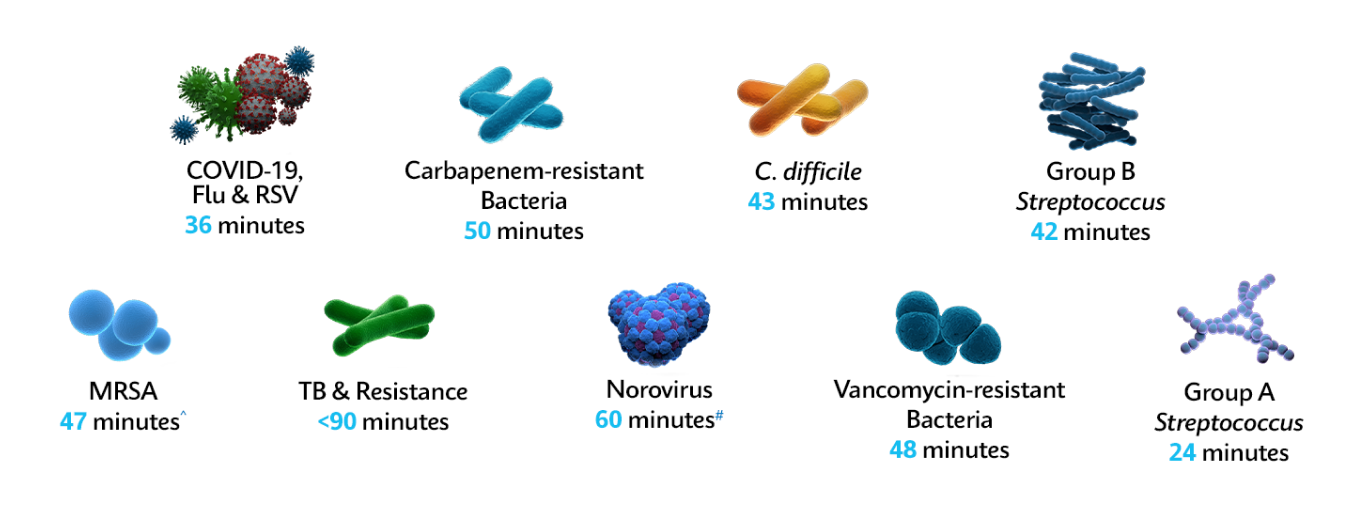
Fight AMR & Superbugs with Fast & Accurate PCR in ~1 Hour*
On-demand identification with the GeneXpert® system's fast PCR Xpert® tests help healthcare professionals reduce onward transmission of resistant bacteria throughout the patient pathway and optimize appropriate therapy management, helping prevent the spread of pathogens and resistance.
Testing in 3 Easy Steps: Sample-In, Answer-Out Technology
1
Insert swab into sample reagent vial and break
2
Transfer sample to cartridge

3
Insert cartridge and start test

Refer to the Cepheid test’s package insert for full details of supported sample types and specimen collection methods
Product Resources

Dr. Fred Tenover: Carbapenemases & Xpert® Carba-R
Dr. Fred Tenover discusses the challenges and solutions to managing the growing threat of CPE, including Xpert® Carba-R, a versatile test that can be used as a surveillance screening test for infection control, an antibiotic resistance test for carbapenemases, and an antimicrobial stewardship tool.

Dr. Fred Tenover: Carbapenemases & Xpert® Carba-R
Dr. Fred Tenover discusses the challenges and solutions to managing the growing threat of CPE, including Xpert® Carba-R, a versatile test that can be used as a surveillance screening test for infection control, an antibiotic resistance test for carbapenemases, and an antimicrobial stewardship tool.
Related Webinars
The Race Against Resistance: Global Perspectives on Tackling AMR
For World AMR Awareness Week 2023, listen back as our global panel share cross-regional expertise, including real-world lived experience of managing outbreaks, meta-analysis and novel diagnostic approaches, in the fight against resistance and threat to last-line antibiotics
Reigniting the AMR Focus Post-COVID-19: Empowering Action with Diagnostics
Join our expert global panel as we examine real-world lived experience, meta-analysis and novel approaches to managing the growing burden of AMR and threat to last-line antibiotics.
Preventing the Spread of Carbapenamase Resistance: A Challenge for Healthcare Now and the Next Decade
Join our expert panel as we discuss the threat behind resistance to last-line antibiotics, real-world lived experience of managing CPE outbreaks, and the role of precision medicine in the fight against resistance.
Tackling a Global Crisis: The Threat Behind Resistance to Last-Line Antibiotics
Listen in as experts discuss the urgency of the underlying threat behind resistance to last-line antibiotics and the overall impact on the fight against AMR.
MRSA: The Where, How, and Why for the Lab; Infection Prevention and Control
In this webinar, listen as experts discuss how rapid and accurate detection of MRSA colonization helps to facilitate targeted infection control practices that can aid workflow to reduce the MRSA transmission and improve overall patient safety.
Carbapenemase Resistance: Understand the Risk. Stop the Growth Trajectory
In this symposium, the speakers will discuss the growing concerns for CREs and the role of screening and management to combat them.
Related Publications
Impact of different carbapenemase-producing Enterobacterales screening strategies in a hospital...
Despite higher initial laboratory PCR costs, savings were made elsewhere through rapidly expediting test results, as well as improving the patient’s experience. A reduction in bed-days lost due to CPE was observed when on-demand molecular screening was introduced.
An outbreak of two strains of OXA-48 producing Klebsiella pneumoniae in a teaching hospital
Reliance on culture and clinical specimens, in particular for OXA-48’s, can be insensitive and lead to late recognition of a problem. Pre-emptive screening of high-risk patients with fast PCR provided an effective and pragmatic solution
Active Surveillance of Carbapenemase-Producing Organisms (CPO) Colonization...
The introduction of on-demand, accurate and easy-to-use PCR testing resulted in a significant decreasing trend in both colonisation and infection rates (p<0.05)
Reducing rates of Clostridium difficile infection by switching to a stand-alone NAAT with clear...
Rapid and sensitive commercial PCR as a stand-alone assay together with clear sampling guidance offers an optimal approach to patient management and best use of limited isolation facilities.
Detection of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infections Using Molecular Methods
While culture methods remain important due to the need for extended antimicrobial susceptibility testing, PCR-based methods offer more rapid results, which reduces the time to optimal antimicrobial therapy
Performance of the Xpert® Carba-R v2 in the daily workflow of a hygiene unit in a country with a low...
On-demand PCR demonstrated excellent performance, and reduced time to result versus culture from 24–48 hours to <1 hour, enabling rapid cohorting of carriers and de-escalation of negative patients. The PCR assay is well adapted for rapid screening of high-risk patients even in low prevalence regions
Can real-time polymerase chain reaction allow a faster recovery of hospital activity in cases of an...
The fast and actionable negative predicative value utilising fast PCR enabled early decision making and avoided the need for x3 weekly culture screening, enabling more appropriate bed management
Evaluation of Xpert Carba-R Assay for the Detection of Carbapenemase Genes in Gram-Negative Bacteria
Meta-analysis performance evaluation concluded the on-demand PCR assay is a proven and efficient methodology for the detection of he “big five” carbapenemase gene families, and could act as the new gold standard
Related Videos

AMR & Carbapenemases
In this short film produced for Cepheid by BBC StoryWorks Commercial Productions and presented by MedTech Europe, Prof. José Artur Paiva (Director, Intensive Care Medicine Service, CHUSJ, Portugal) discusses the important role of fast PCR testing in fighting the growing threat of AMR and CPE.

Carbapenemases
Dr. Tim Neal, Infection Control Doctor at Liverpool Clinical Laboratories, details how fast molecular diagnostic solutions are critical to staying ahead of the emerging threat of CPE.

Carbapenemases
Dr. Thierry Nass, Co-Director of the French National Reference Center for Antibiotic Resistance, details the increasing global threat of CPE, and growing role of fast molecular testing to identify and limit the spread of resistance.

AMR & Carbapenemases
In this short film produced for Cepheid by BBC StoryWorks Commercial Productions and presented by MedTech Europe, Prof. José Artur Paiva (Director, Intensive Care Medicine Service, CHUSJ, Portugal) discusses the important role of fast PCR testing in fighting the growing threat of AMR and CPE.

Carbapenemases
Dr. Tim Neal, Infection Control Doctor at Liverpool Clinical Laboratories, details how fast molecular diagnostic solutions are critical to staying ahead of the emerging threat of CPE.

Carbapenemases
Dr. Thierry Nass, Co-Director of the French National Reference Center for Antibiotic Resistance, details the increasing global threat of CPE, and growing role of fast molecular testing to identify and limit the spread of resistance.
PCR Tools to Fight AMR

Xpert® SA Nasal Complete
References
CE-IVD In Vitro Diagnostic Medical Device. May not be available
in all countries.
* Turnaround times vary by test. See individual Product Inserts for
specific turnaround times.
^ For positive MRSA results with early assay termination. Otherwise, full
runtime is 70 minutes.
# For positive Norovirus results with early assay termination. Otherwise,
full runtime is 90 minutes.
- World Healt Organization (WHO). 2019. New report calls for urgent action to avert antimicrobial resistance crisish. Accessed March 2022. https://www.who.int/news/item/29-04-2019-new-report-calls-for-urgent-action-to-avert-antimicrobial-resistance-crisis
- Murray C, et al. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: a systematic analysis. The Lancet. 2022 Feb;399(10325):629-655
- WHO. 2017. The World is Running Out of Antibiotics, WHO Report Confirms. Accessed Sep 2023. https://www.who.int/news/item/20-09-2017-the-world-is-running-out-of-antibiotics-who-report-confirms
- ECDC. 2019. Antimicrobial Resistance: Tackling the Burden in the European Union. Accessed Feb 2023. https://www.oecd.org/health/health-systems/AMR-Tackling-the-Burden-in-the-EU-OECD-ECDC-Briefing-Note-2019.pdf
- MedTech Europe. 2014. Healthcare-Associated Infections Brochure. Accessed Feb 2021. https://www.medtecheurope.org/resource-library/hai-brochure/
- Langford B, et al. Bacterial co-infection and secondary infection in patients with COVID-19: a living rapid review and meta-analysis. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020 Dec;26(12):1622-1629
- Belvisi V, et al. Impact of severe acute respiratory syndrome coro navirus-2 (SARS CoV-2) pandemic on carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae (KPC-Kp) prevention and control program: convergent or divergent action? J Hosp Infect. 2020 Dec;109:29-31
- Pritchard M, et al. International Severe Acute Respiratory and Emerging Infections Consortium, COVID-19 Report: 8 June 2020. medRxiv. Accessed Feb 2021. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/343217999_ISARIC_COVID-19_Clinical_Data_Report_8_June_2020
- Laboratory testing for coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in suspected human cases: interim guidance, 19 March 2020. Accessed November 2022. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/331501
- Otter J, et al. Counting the cost of an outbreak of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae: an economic evaluation from a hospital perspective. CMI. 2016 Oct;23(3):188-196.



